Produkte
-

Elecrow CrowBot BOLT – Smart Robot Car Kit (mit Joystick)
CrowBot BOLT ist ein ESP32-gesteuertes, intelligentes, einfaches und benutzerfreundliches Open-Source-Roboterauto. Es ist mit den Arduino- und MicroPython-Umgebungen kompatibel und bietet grafische Programmierung über Letscode. Es stehen 16 Lernkurse mit interessanten Experimenten zur Verfügung. Features 16 Lektionen in drei Sprachen (Letscode, Arduino, Micropython) für schnelles Lernen und unterhaltsame Experimente. Kompatibel mit Arduino, MicroPython-Entwicklungsumgebung, mit grafischer Letscode-Programmierung. Starke Skalierbarkeit mit einer Vielzahl von Schnittstellen, erweiterbar und mit Crowtail-Modulen nutzbar. Eine Vielzahl von Fernbedienungsmodi: Sie können das Auto mit der Infrarot-Fernbedienung und dem Joystick steuern. Technische Daten Prozessor ESP32-Wrover-B (8 MB) Programmierung Letscode, Arduino, Micropython Steuermethode Bluetooth-Fernbedienung/Infrarot-Fernbedienung Eingabe Taste, Lichtsensor, Infrarot-Empfangsmodul, Ultraschallsensor, Linienverfolgungssensor Ausgabe Summer, programmierbares RGB-Licht, Motor WLAN & Bluetooth Ja Lichtsensor Kann die Funktion erfüllen, Licht zu jagen oder Licht zu meiden Ultraschallsensor Wenn ein Hindernis erkannt wird, kann die Fahrtroute des Fahrzeugs korrigiert werden, um dem Hindernis auszuweichen Linienverfolgungssensor Kann das Auto entlang der dunklen/schwarzen Linien bewegen lassen, den Fahrweg intelligent beurteilen und korrigieren Summer Kann das Auto ertönen/pfeifen lassen und so ein direkteres Sinneserlebnis bieten Programmierbares RGB-Licht Durch Programmierung können bunte Lichter in verschiedenen Szenen angezeigt werden Infrarotempfänger Empfangen Sie Infrarot-Fernbedienungssignale, um die Fernbedienung zu realisieren Schnittstellen 1x USB-C, 1x I²C, 1x A/D Motortyp GA12-N20 Mikro-DC-Getriebemotor Betriebstemperatur -10℃~+55℃ Stromversorgung 4x 1,5 V Batterien (nicht im Lieferumfang enthalten) Akkulaufzeit 1,5 Stunden Abmessungen 128 x 92 x 64 mm Gewicht 900 g Lieferumfang 1x Gehäuse 1x Ultraschallsensor 1x Batteriehalter 2x Räder 4x M3x8 mm Schrauben 2x M3x5 mm Kupfersäule 2x Seitliche Acrylplatten 1x Vordere Acrylplatten 1x Schraubendreher 2x 4-poliges Crowtail-Kabel 1x USB-C Kabel 1x Infrarot-Fernbedienung 1x Anleitung & Linien-Gleiskarte 1x Joystick Downloads Wiki CrowBot-BOLT_Assembly-Instruction Joystick-for-CrowBot-BOLT_Assembly-Instruction CrowBot_BOLT_Beginner’s_Guide Designing Documents of CrowBot Designing Documents of Joystick Lesson Code 3D Model Factory Source Code
-

Elecrow Crowtail-4G SIM A7670E Modul GPS Breakout Board
Dieses 4G-Modul der Crowtail-Serie ist ein leistungsstarkes LTE Cat1-Funkmodul. Es nutzt das Kommunikationsmodul SIM A7670E von Simcom und kommuniziert über eine UART-Schnittstelle, die 4G-Datenübertragung und Sprachkommunikation ermöglicht. Das Modul unterstützt mehrere LTE-Bänder, einschließlich B1/B3/B5/B7/B8/B20, sowie WCDMA- und GSM-Netze. Darüber hinaus unterstützt es verschiedene Protokolle wie TCP/IP, FTP, HTTP und mehrere Satellitennavigationssysteme wie GPS, GLONASS und BDS. Das Modul verfügt über eine Ladeschnittstelle und kann mit einer 3,7 V Lithiumbatterie oder einer 5 V USB-C-Schnittstelle betrieben werden. Es verfügt außerdem über einen 3,5-mm-Kopfhöreranschluss und kann durch den Anschluss eines Kopfhörers mit Mikrofon zum Tätigen und Empfangen von Telefonanrufen verwendet werden. Seine kompakte Größe erleichtert die Integration in verschiedene IoT-Geräte und erfüllt verschiedene Anwendungsanforderungen. Darüber hinaus sind sein geringer Stromverbrauch und seine zuverlässige Leistung auch die Gründe, warum es in den Bereichen IoT, Smart Home, Automobil und Industriesteuerung weit verbreitet ist. Features Integrieren Sie das A7670E-Kommunikationsmodul und ermöglichen Sie 4G-Datenübertragung und Sprachkommunikation mit geringem Stromverbrauch und hoher Zuverlässigkeit Unterstützt mehrere LTE-Bänder, einschließlich B1/B3/B5/B7/B8/B20, sowie WCDMA- und GSM-Netzwerke Unterstützt verschiedene Protokolle wie TCP/IP, FTP, HTTP und mehrere Satellitennavigationssysteme wie GPS, GLONASS und BDS Verfügt über eine Ladeschnittstelle und einen Kopfhöreranschluss, der zum Tätigen und Empfangen von Telefonanrufen verwendet werden kann, indem ein Kopfhörer mit Mikrofon angeschlossen wird Klein, aber leistungsstark, die kompakte Größe erleichtert die Integration in verschiedene IoT-Geräte. Technische Daten Hauptchip: SIM A7670E LTE-FDD: B1/B3/B5/B7/B8/B20 GSM: 900/1800 MHz GSM/GPRS-Leistungsklasse EGSM900: 4 (33 dBm ±2 dB) DCS1800: 1 (30 dBm ±2 dB) EDGE-Leistungsklasse: EGSM900: E2 (27 dBm ±3 dB) DCS1800: E1 (26 dBm +3 dB/-4 dB) LTE-Leistungsklasse: 3 (23 dBm ±7 dB) Versorgungsspannung: 4 V ~ 4,2 V Stromversorgung: 3,8 V LTE(Mbps): 10(DL)/5(UL) GPRS/EDGE (Kbit/s): 236,8 (DL)/236,8 (UL) Protokoll: TCP/IP/IPV4/IPV6/Multi-PDP/FTP/FTPS /HTTP/HTTPS/DNS Kommunikationsschnittstelle: USB / UART Firmware-Upgrade: USB/FOTA Unterstützte Telefonbuchtypen: SM/FD/ON/AP/SDN Schnittstellen: 1x Power-Taste, 1x BAT, 1x UART, 1x USB-C, 1x SIM-Kartensteckplatz Abmessungen: 35 x 50 mm Lieferumfang 1x Crowtail-4G SIM-A7670E 1x 4G GSM NB-IoT-Antenne 1x GPS-Keramikantenne Downloads Wiki A7670 AT Command Manual A7670 Datasheet Source Code
-

Elecrow CrowVi 13,3" IPS HD-Touchdisplay (1920x1080)
Heutzutage verwenden immer mehr und intelligentere Telefone und Laptops USB-C-Anschlüsse wegen ihrer leistungsstarken Funktion, mit der Strom, Daten und Videoinformationen übertragen werden können. Durch die USB-C-Lösung kann das Gerät im Vergleich zum Thunderbolt 3- oder HDMI-kompatiblen Anschluss auch viel dünner werden. Aus diesem Grund haben wir den tragbaren USB-C-Monitor CrowVi entwickelt.Der superdünne CrowVi 13,3-Zoll-Monitor verfügt über 2 USB-C-Anschlüsse, einer dient der Stromversorgung und der andere dient der Datenübertragung von Video- und Touchscreen-Befehlen. Der Bildschirm kann auch über den Mini-HDMI-kompatiblen Anschluss angeschlossen werden Port. Die Auflösung von CrowVi beträgt 1920x1080, was ein besseres Erlebnis beim Spielen und Ansehen von Filmen bietet.FeaturesDas CrowVi-Gehäuse besteht aus einer Aluminiumlegierung, ist nur 5 mm dick und der Bildschirmrand ist nur 6 mm schmal. Der gesamte Monitor sieht exquisit und elegant aus.CrowVi kann nicht nur als Dual-Monitor für Smartphones und Laptops fungieren, sondern auch als Einzelmonitor für Gaming-Geräte und einige Computer-Mainframes wie Mac mini, Raspberry Pi usw.CrowVi bietet Ihnen im Vergleich zum Smartphone eine viel größere Ansicht. Es ermöglicht bessere Erlebnisse beim Spielen und Ansehen von Filmen.Technische DatenBildschirm13,3' TFT IPS LCDBildschirmgröße294,5 x 164 mmDicke5-10 mmAuflösung1920 x 1080Helligkeit300 NitsAktualisierungsrate60 HzFarbraum16,7 Mio., NTSC 72%, sRGB bis zu 100%Kontrast800:1HintergrundbeleuchtungLEDBetrachtungswinkel178°Seitenverhältnis16:9SprecherZwei Lautsprecher 8 Ω, 2 WShellAluminiumlegierungEingabeMini-HD, USB-C, PDAusgabe3,5-mm-KopfhöreranschlussMachtPD 5-20 V oder USB-C 3.0Betriebstemperatur0-50°CAbmessungen313 x 198 x 10 mmGewicht (Smart Case)350 gGewicht (Monitor)700 gLieferumfang13,3-Zoll-Touchscreen-MonitorIntelligentes GehäuseUSB-C-auf-USB-C-Kabel (1 m)USB-A-zu-USB-C-Stromkabel (1 m)HDMI-zu-Mini-HDMI-Kabel (1 m)Netzteil (5 V/2 A)HDMI-zu-Mini-HDMI-AdapterStaubtuchHandbuchDownloadsUser manual
-

Heltec Automation CubeCell HTCC-AB01 (V2) LoRa Development Board (EU868)
The CubeCell series is designed primarily for LoRa/LoRaWAN node applications. Built on the ASR605x platform (ASR6501, ASR6502), these chips integrate the PSoC 4000 series MCU (ARM Cortex-M0+ Core) with the SX1262 module. The CubeCell series offers seamless Arduino compatibility, stable LoRaWAN protocol operation, and straightforward connectivity with lithium batteries and solar panels. The HTCC-AB01 (V2) is an upgraded version of the HTCC-AB01 board. Features Arduino compatible Based on ASR605x (ASR6501, ASR6502), those chips are already integrated the PSoC 4000 series MCU (ARM Cortex-M0+ Core) and SX1262 LoRaWAN 1.0.2 support Ultra low power design, 3.5 uA in deep sleep Onboard SH1.25-2 battery interface, integrated lithium battery management system (charge and discharge management, overcharge protection, battery power detection, USB/battery power automatic switching) Good impendence matching and long communication distance. Onboard solar energy management system, can directly connect with a 5.5~7 V solar panel Micro USB interface with complete ESD protection, short circuit protection, RF shielding, and other protection measures Integrated CP2102 USB to serial port chip, convenient for program downloading, debugging information printing Specifications Main Chip ASR6502 (48 MHz ARM Cortex-M0+ MCU) LoRa Chipset SX1262 Frequency 863~870 MHz Max. TX Power 21 ±1 dBm Max. Receiving Sensitivity −134 dBm Hardware Resource 1x UART1x SPI1x I²C1x SWD1x 12-bit ADC input8-channel DMA engine8x GPIO2x PWM Memory 128 Kb FLASH16 Kb SRAM Power consumption Deep Sleep 3.5 uA Interfaces 1x USB-C1x LoRa Antenna (IPEX 1.0)SH1.25; 11x 2x 2.54 Pin header1x (2x 2.54 Pin header) Solar Energy VS pin can be connected to 5.5~7 V solar panel Battery 3.7 V Lithium battery (power supply and charging) Operating temperature −20~70°C Dimensions 40.6 x 22.9 x 7.6 mm Included 1x CubeCell HTCC-AB01 (V2) Development Board 1x Antenna 1x 2x SH1.25 battery connector Downloads Datasheet Schematic Quick start GitHub
-

Heltec Automation CubeCell HTCC-AB02 LoRa Development Board (EU868)
The CubeCell series is designed primarily for LoRa/LoRaWAN node applications. Built on the ASR605x platform (ASR6501, ASR6502), these chips integrate the PSoC 4000 series MCU (ARM Cortex-M0+ Core) with the SX1262 module. The CubeCell series offers seamless Arduino compatibility, stable LoRaWAN protocol operation, and straightforward connectivity with lithium batteries and solar panels. The HTCC-AB02 is a developer-friendly board, ideal for quickly testing and validating communication solutions. Features Arduino compatible Based on ASR605x (ASR6501, ASR6502), those chips are already integrated the PSoC 4000 series MCU (ARM Cortex M0+ Core) and SX1262 LoRaWAN 1.0.2 support Ultra low power design, 3.5 uA in deep sleep Onboard SH1.25-2 battery interface, integrated lithium battery management system (charge and discharge management, overcharge protection, battery power detection, USB/battery power automatic switching) Good impendence matching and long communication distance Onboard solar energy management system, can directly connect with a 5.5~7 V solar panel Micro USB interface with complete ESD protection, short circuit protection, RF shielding, and other protection measures Integrated CP2102 USB to serial port chip, convenient for program downloading, debugging information printing Onboard 0.96-inch 128x64 dot matrix OLED display, which can be used to display debugging information, battery power, and other information Specifications Main Chip ASR6502 (48 MHz ARM Cortex-M0+ MCU) LoRa Chipset SX1262 Frequency 863~870 MHz Max. TX Power 22 ±1 dBm Max. Receiving Sensitivity −135 dBm Hardware Resource 2x UART1x SPI2x I²C1x SWD3x 12-bit ADC input8-channel DMA engine16x GPIO Memory 128 Kb FLASH16 Kb SRAM Power consumption Deep sleep 3.5 uA Interfaces 1x Micro USB1x LoRa Antenna (IPEX)2x (15x 2.54 Pin header) + 3x (2x 2.54 Pin header) Battery 3.7 V lithium battery (power supply and charging) Solar Energy VS pin can be connected to 5.5~7 V solar panel USB to Serial Chip CP2102 Display 0.96" OLED (128 x 64) Operating temperature −20~70°C Dimensions 51.9 x 25 x 8 mm Included 1x CubeCell HTCC-AB02 Development Board 1x Antenna 1x 2x SH1.25 battery connector Downloads Datasheet Schematic Quick start GitHub
-
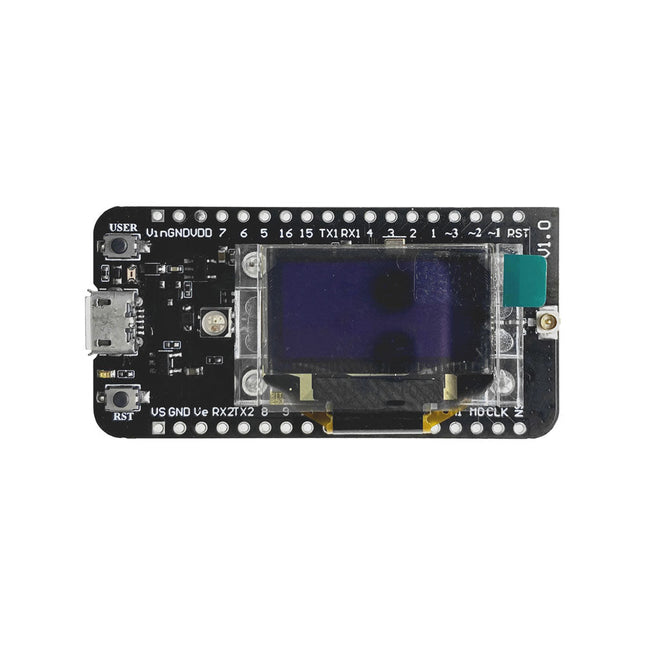
Heltec Automation CubeCell HTCC-AB02S LoRa Development Board with GPS (EU868)
The CubeCell series is designed primarily for LoRa/LoRaWAN node applications. Built on the ASR605x platform (ASR6501, ASR6502), these chips integrate the PSoC 4000 series MCU (ARM Cortex-M0+ Core) with the SX1262 module. The CubeCell series offers seamless Arduino compatibility, stable LoRaWAN protocol operation, and straightforward connectivity with lithium batteries and solar panels. The HTCC-AB02S is a developer-friendly board with an integrated AIR530Z GPS module, ideal for quickly testing and validating communication solutions. Features Arduino compatible Based on ASR605x (ASR6501, ASR6502), those chips are already integrated the PSoC 4000 series MCU (ARM Cortex M0+ Core) and SX1262 LoRaWAN 1.0.2 support Ultra low power design, 21 uA in deep sleep Onboard SH1.25-2 battery interface, integrated lithium battery management system (charge and discharge management, overcharge protection, battery power detection, USB/battery power automatic switching) Good impendence matching and long communication distance Onboard solar energy management system, can directly connect with a 5.5~7 V solar panel Micro USB interface with complete ESD protection, short circuit protection, RF shielding, and other protection measures Integrated CP2102 USB to serial port chip, convenient for program downloading, debugging information printing Onboard 0.96-inch 128x64 dot matrix OLED display, which can be used to display debugging information, battery power, and other information Using Air530 GPS module with GPS/Beidou Dual-mode position system support Specifications Main Chip ASR6502 (48 MHz ARM Cortex-M0+ MCU) LoRa Chipset SX1262 Frequency 863~870 MHz Max. TX Power 22 ±1 dBm Max. Receiving Sensitivity −135 dBm Hardware Resource 2x UART1x SPI2x I²C1x SWD3x 12-bit ADC input8-channel DMA engine16x GPIO Memory 128 Kb FLASH16 Kb SRAM Power consumption Deep sleep 21 uA Interfaces 1x Micro USB1x LoRa Antenna (IPEX)2x (15x 2.54 Pin header) + 3x (2x 2.54 Pin header) Battery 3.7 V lithium battery (power supply and charging) Solar Energy VS pin can be connected to 5.5~7 V solar panel USB to Serial Chip CP2102 Display 0.96" OLED (128 x 64) Operating temperature −20~70°C Dimensions 55.9 x 27.9 x 9.5 mm Included 1x CubeCell HTCC-AB02S Development Board 1x Antenna 1x 2x SH1.25 battery connector Downloads Datasheet Schematic GPS module (Manual) Quick start GitHub
€ 49,95€ 24,95
Mitglieder identisch
-

Cytron Cytron Maker Line Sensor
Maker Line ist ein Zeilensensor mit einem Array aus 5 IR-Sensoren, der Linien mit einer Breite von 13 mm bis 30 mm verfolgen kann. Auch die Sensorkalibrierung wird vereinfacht. Es ist nicht mehr nötig, das Potentiometer für jeden einzelnen IR-Sensor einzustellen. Sie müssen nur die Kalibrierungstaste 2 Sekunden lang drücken, um in den Kalibrierungsmodus zu wechseln. Anschließend müssen Sie das Sensorarray über die Linie bewegen, die Taste erneut drücken und schon kann es losgehen. Die Kalibrierungsdaten werden im EEPROM gespeichert und bleiben auch nach dem Ausschalten des Sensors erhalten. Die Kalibrierung muss daher nur einmal durchgeführt werden, es sei denn, die Sensorhöhe, Linienfarbe oder Hintergrundfarbe hat sich geändert. Maker Line unterstützt auch zwei Ausgänge: 5 x digitale Ausgänge für den Zustand jedes Sensors unabhängig voneinander, was einem herkömmlichen IR-Sensor ähnelt, aber Sie profitieren von der einfachen Kalibrierung, und auch ein analoger Ausgang, dessen Spannung die Linienposition darstellt. Der analoge Ausgang bietet auch eine höhere Auflösung im Vergleich zu einzelnen digitalen Ausgängen. Dies ist besonders nützlich, wenn beim Bau eines Linienverfolgungsroboters mit PID-Steuerung eine hohe Genauigkeit erforderlich ist. Features Betriebsspannung: DC 3,3 V und 5 V kompatibel (mit Verpolungsschutz) Empfohlene Linienbreite: 13 mm bis 30 mm Wählbare Linienfarbe (hell oder dunkel) Erfassungsabstand (Höhe): 4 mm bis 40 mm (Vcc = 5 V, schwarze Linie auf weißer Oberfläche) Sensor-Aktualisierungsrate: 200 Hz Einfacher Kalibrierungsprozess Duale Ausgabetypen: 5 x digitale Ausgänge repräsentieren jeden IR-Sensorstatus, 1 x analoger Ausgang repräsentiert die Zeilenposition. Unterstützt eine breite Palette von Controllern wie Arduino, Raspberry Pi usw. Downloads Datenblatt Tutorial: Einen kostengünstigen Linienverfolgungsroboter bauen
€ 14,95€ 7,50
Mitglieder identisch
-

Cytron Cytron Maker pHAT für Raspberry Pi
Der Maker pHAT ist die Lösung für die häufigsten Probleme, mit denen Einsteiger beim Einstieg in Raspberry PI konfrontiert sind. Sein intelligentes und einfaches Design erleichtert die Anbringung an Ihrem Pi und erspart Ihnen die mühsame Arbeit, verschiedene andere Zubehörteile anzuschließen. Darüber hinaus können Sie anhand der jedem Pin zugeordneten LEDs ganz einfach erkennen, wo ein potenzielles Problem liegt Der Maker pHat hat die gleiche Größe wie der Raspberry Pi Zero, wobei alle 4 Befestigungslöcher ausgerichtet sind. Es kann jedoch mit Raspberry Pi 3B, 3B+ und 3A+ verwendet werden, indem ein 2 x 20-Stacking-Header eingesetzt wird. Merkmale Raspberry Pi Zero-Größe, lässt sich perfekt auf Raspberry Pi Zero stapeln Kompatibel mit Raspberry Pi 3B / 3B+ in Standardgröße, Raspberry Pi 3A+ in mittlerer Größe und Raspberry Pi Zero / W / WH in kleinerer Größe. Standard-GPIO-Footprint des Raspberry Pi. LED-Array für ausgewählte GPIO-Pins (GPIO 17, 18, 27, 22, 25, 12, 13, 19). 3x integrierte programmierbare Drucktasten (GPIO 21, 19 und 20, müssen als Eingangs-Pullup konfiguriert werden). Integrierter aktiver Summer (GPIO 26). Richtige Bezeichnungen für alle GPIOs, einschließlich SPI, UART, I2C, 5V, 3,3V und GND. Nutzen Sie die USB-Micro-B-Buchse für den 5-V-Eingang und die USB-zu-UART-Kommunikation. USB seriell ermöglicht durch den FT231X Eingangsspannung: USB 5 V, von einem Computer, einer Powerbank oder einem Standard-USB-Adapter. Montage auf Raspberry Pi Zero Montage auf Raspberry Pi 3B, 3B+ und 3A+
€ 14,95
Mitglieder € 13,46
-
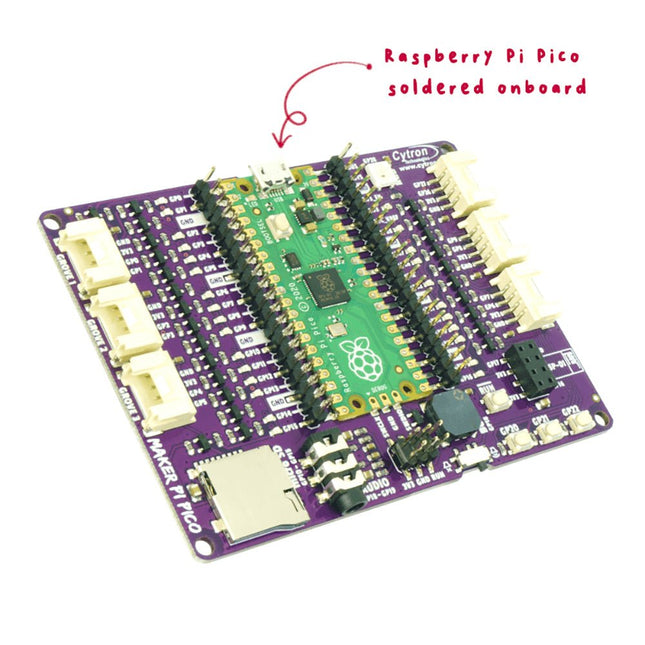
Cytron Cytron Maker Pi Pico (mit vorgelötetem Raspberry Pi Pico)
Der Cytron Maker Pi Pico (mit vorgelötetem Raspberry Pi Pico RP2040) enthält die am meisten gewünschten Funktionen für Ihren Raspberry Pi Pico und bietet Ihnen Zugang zu allen GPIO-Pins auf zwei 20-poligen Stiftleisten mit eindeutigen Beschriftungen. Jede GPIO ist mit einer LED-Anzeige gekoppelt, die das Testen des Codes und die Fehlersuche erleichtert. Die untere Ebene dieses Boards enthält sogar ein umfassendes Pinbelegungsdiagramm, das die Funktion jedes Pins zeigt. Features Sofort einsatzbereit. Kein Löten! Zugriff auf alle Pins von Raspberry Pi Pico auf zwei 20-poligen Stiftleisten LED-Anzeigen an allen GPIO-Pins 3x programmierbarer Taster (GP20-22) 1x RGB-LED – NeoPixel (GP28) 1x Piezo-Summer (GP18) 1x 3,5-mm-Stereo-Audiobuchse (GP18-19) 1x Micro-SD-Kartensteckplatz (GP10-15) 1x ESP-01 Sockel (GP16-17) 6x Grove-Schnittstelle Technische Daten Prozessor 32-bit ARM Cortex-M0+ Prozessortakt 48 MHz, bis zu 133 MHz Flashspeicher 2 MByte Q-SPI Flash Programmiersprache MicroPython, C++ Stromversorgung 5 VDC via MicroUSB Alternative Stromversorgung 2-5 VDC via VSYS Pin (Pin 39) MCU-Spannung 3,3 VDC GPIO-Spannung 3,3 VDC USB-Schnittstelle USB 1.1 Device Host Programladen MicroUSB, USB-Massenspeicher GPIO 26x Ein-/Ausgang ADC 3x 12-bit 500 ksps Temperatursensor Eingebaut, 12-bit UART 2x UART I²C 2x I²C SPI 2x SPI PWM 16x PWM Timer 1x Timer mit 4 x Alarm Echtzeitzähler 1x Echtzeitzähler PIO 2x Programmierbare High-Speed I/O On-Board LED 1x Programmierbare LED On-Board Button 1x BOOTSEL Button
€ 24,95€ 19,95
Mitglieder identisch
-

Cytron Cytron Maker Pi Pico Mini W (mit vorgelötetem Raspberry Pi Pico W und vorinstalliertem CircuitPython)
Lieben Sie den Cytron Maker Pi Pico (SKU 19706), können ihn aber nicht in Ihr Projekt integrieren? Jetzt gibt es den Cytron Maker Pi Pico Mini W. Er wird von dem fantastischen Raspberry Pi Pico W betrieben und hat die meisten nützlichen Funktionen seines größeren Geschwisters geerbt, wie z. B. GPIO-Status-LEDs, WS2812B Neopixel RGB-LED, passiven Piezo-Summer und nicht zu vergessen die Benutzer- und Zurücksetzen-Taste. Funktionen Powered by Raspberry Pi Pico W Einzelliger LiPo-Anschluss mit Überladungs- / Tiefentladungsschutzschaltung, aufladbar über USB. 6x Statusindikator-LEDs für GPIOs 1x Passiver Piezo-Summer (kann Musikton oder Melodie abspielen) 1x Zurücksetzen-Taste 1x Benutzerprogrammierbare Taste 1x RGB-LEDs (WS2812B Neopixel) 3x Maker-Anschlüsse, kompatibel mit Qwiic, STEMMA QT und Grove (über Konvertierungskabel) Unterstützung für Arduino IDE, CircuitPython und MicroPython Abmessungen: 23,12 x 53,85 mm Im Lieferumfang enthalten 1x Maker Pi Pico Mini W (vorgefertigter Raspberry Pi Pico W mit vorinstalliertem CircuitPython) 3x Grove to JST-SH (Qwiic / STEMMA QT) Kabel Downloads Maker Pi Pico Mini Datenblatt Maker Pi Pico Mini Schaltplan Maker Pi Pico Mini Pinout-Diagramm Offizielle Raspberry Pi Pico-Seite Erste Schritte mit dem Raspberry Pi Pico CircuitPython für Raspberry Pi Pico Raspberry Pi Pico Datenblatt RP2040 Datenblatt Raspberry Pi Pico Python SDK Raspberry Pi Pico C/C++ SDK
€ 19,95€ 16,95
Mitglieder identisch
-

Cytron Cytron Maker Uno
Merkmale Piezo-Summer: Fungiert als einfacher Audioausgang Micro-USB-Anschluss Programmierbare Taste 12 x LED: Bietet visuelle Ausgabe an Bord Spezifikationen Mikrocontroller ATmega328P Programmier-IDE Arduino IDE Betriebsspannung 5 V Digitale E/A 20 PWM 6 Analoger Eingang 6 (10 Bit) UART 1 SPI 1 I2C 1 Externer Interrupt 2 Flash-Speicher 32 KB SRAM 2 KB EEPROM / Daten-Flash 1 KB Taktfrequenz 16 MHz Gleichstrom-E/A-Pin 20 mA Stromversorgung Nur USB Gleichstrom für 5 V USB-Quelle Gleichstrom für 3,3 V 500 mA USB-zu-Seriell-Chip CH340G Programmierbare LED 12 an Digital Pin 2 bis 13 Programmierbarer Druckknopf 1 am digitalen Pin 2 Piezo-Summer 1 am digitalen Pin 8 Arduino gegen Maker Uno
€ 14,95
Mitglieder € 13,46
-
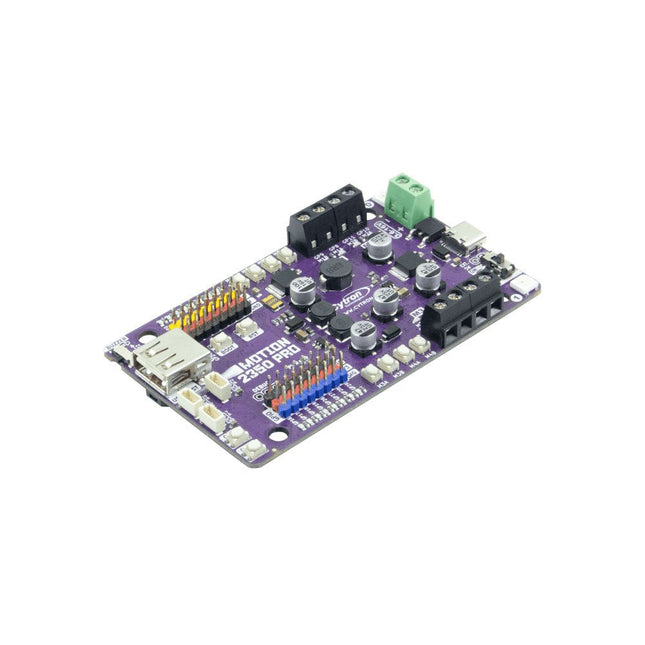

Cytron Cytron Motion 2350 Pro Roboter-Controller
Der Cytron Motion 2350 Pro ist ein robuster 4-Kanal-DC-Motortreiber (3 A pro Kanal, 3,6–16 V), der sich ideal für den Bau leistungsstarker Roboter, einschließlich Mecanum-Raddesigns, eignet. Es verfügt über 8-Kanal-5-V-Servoanschlüsse, 8-Kanal-GPIO-Breakouts, 3 Maker-Anschlüsse und einen USB-Host für Plug-and-Play-Joystick-/Gamepad-Unterstützung. Angetrieben durch Raspberry Pi Pico 2 lässt es sich nahtlos in das Pico-Ökosystem integrieren und unterstützt Python (MicroPython, CircuitPython), C/C++ und Arduino IDE. Es ist mit CircuitPython vorinstalliert und verfügt über ein Demoprogramm und Schnelltestschaltflächen für den sofortigen Einsatz. Einfach über USB-C anschließen und los geht’s! Lieferumfang 1x Cytron Motion 2350 Pro Roboter-Controller 1x STEMMA QT/Qwiic JST SH 4-poliges Kabel mit Buchsen (150 mm) 2x Grove-zu-JST-SH-Kabel (200 mm) 1x Set Silikon-Stoßfänger 4x Baustein-Reibstift 1x Mini-Schraubendreher
€ 29,95€ 24,95
Mitglieder identisch
-

Cytron Cytron REKA:BIT – Robotik mit micro:bit
Programmieren Sie Ihr REKA:BIT mit dem Microsoft MakeCode Editor . Fügen Sie einfach die REKA:BIT MakeCode-Erweiterung hinzu und schon kann es losgehen. Wenn Sie ein Anfänger sind, können Sie mit dem Blockprogrammierungsmodus beginnen. Ziehen Sie einfach die Codierungsblöcke per Drag-and-Drop und rasten Sie sie zusammen. Fortgeschrittenere Benutzer können im MakeCode Editor für die textbasierte Programmierung problemlos in den JavaScript- oder Python-Modus wechseln. REKA:BIT verfügt über zahlreiche Anzeige-LEDs, die Sie bei der Codierung und Fehlerbehebung unterstützen. Es deckt die E/A-Pins ab, die mit allen sechs Grove-Ports und den Gleichstrommotorausgängen des Coprozessors verbunden sind. Durch die Überwachung dieser LEDs kann man sein Programm und seine Schaltkreisverbindung leicht überprüfen. Darüber hinaus verfügt REKA:BIT über eine Ein-/Aus-Anzeige sowie integrierte Unterspannungs- und Überspannungs-LEDs, um bei Problemen mit der Stromversorgung entsprechende Warnungen auszugeben. REKA:BIT verfügt über einen Co-Prozessor, um Multitasking effizienter zu bewältigen. Musik abzuspielen und gleichzeitig bis zu 4 Servomotoren und 2 Gleichstrommotoren zu steuern, die micro:bit LED-Matrix zu animieren und sogar RGB-LEDs in verschiedenen Farben gleichzeitig zum Leuchten zu bringen, ist für REKA:BIT kein Problem. Features 2x DC-Motorklemmen Integrierte Motor-Schnelltesttasten (keine Codierung erforderlich) 4x Servomotoranschlüsse 2x Neopixel RGB-LEDs 6x Grove-Port (3,3 V) 3x Analogeingang/Digital-IO-Ports 2x digitale IO-Ports 1x I²C-Schnittstelle DC-Buchse für Stromeingang (3,6 – 6 VDC) Ein / Aus Schalter Einschaltanzeige Unterspannungsanzeige (LOW) und Schutz Überspannungsanzeige (HIGH) und Schutz Abmessungen: 10,4 x 72 x 15 mm Lieferumfang 1x REKA:BIT Erweiterungsplatine 1x USB-Strom- und Datenkabel 1x 4xAA Batteriehalter 1x Mini-Schraubendreher 3x Grove-auf-Buchsen-Header-Kabel 2x Baustein 1x9 Hubarm 4x Baustein-Reibstift Bitte beachten Sie : micro:bit-Platine nicht im Lieferumfang enthalten
€ 22,95
Mitglieder € 20,66
-

Elektor Publishing Das 1-Wire-Praxisbuch
1-Wire ist die Bezeichnung für eine serielle Schnittstelle, die mit nur einer Datenader auskommt. Es ist ein Master-Multi-Slave-Kommunikationsprotokoll. Verfügbar sind integrierte Bausteine zur Temperaturmessung, Akkuüberwachung, Echtzeituhr und beispielsweise Hotelschließanlagen. Eine Besonderheit von 1-Wire-Geräten ist die Spannungsversorgung aus der Gegenstation, hierbei erfolgt die Versorgung der Slaves über die Datenleitung. Der Leser erhält mit „Das 1-Wire-Praxisbuch“ eine umfassende Einführung in die 1-Wire-Technologie. Das Buch zeigt anhand praktischer Projekte zum Nachbauen, wie man verschiedene verfügbare 1-Wire-Chips in eigene Mikrocontroller-gesteuerte Anwendungen integrieren kann, und zwar mit Assembler-Software-Implementierungen für PIC-Mikrocontroller und mit Sketches für den Arduino. Die 1-Wire-Technik kommt in dem Buch praxisnah bei einem elektronischen Schloss zum Einsatz, das von einem PIC-Mikrocontroller gesteuert wird. Ein weiteres Praxisprojekt erläutert Schritt für Schritt, wie beispielsweise eine ständige Temperaturmessung mit 1-Wire-Bausteinen möglich ist.
€ 39,80
Mitglieder identisch
-

Elektor Digital Das 1-Wire-Praxisbuch (PDF)
1-Wire ist die Bezeichnung für eine serielle Schnittstelle, die mit nur einer Datenader auskommt. Es ist ein Master-Multi-Slave-Kommunikationsprotokoll. Verfügbar sind integrierte Bausteine zur Temperaturmessung, Akkuüberwachung, Echtzeituhr und beispielsweise Hotelschließanlagen. Eine Besonderheit von 1-Wire-Geräten ist die Spannungsversorgung aus der Gegenstation, hierbei erfolgt die Versorgung der Slaves über die Datenleitung. Der Leser erhält mit „Das 1-Wire-Praxisbuch“ eine umfassende Einführung in die 1-Wire-Technologie. Das Buch zeigt anhand praktischer Projekte zum Nachbauen, wie man verschiedene verfügbare 1-Wire-Chips in eigene Mikrocontroller-gesteuerte Anwendungen integrieren kann, und zwar mit Assembler-Software-Implementierungen für PIC-Mikrocontroller und mit Sketches für den Arduino. Die 1-Wire-Technik kommt in dem Buch praxisnah bei einem elektronischen Schloss zum Einsatz, das von einem PIC-Mikrocontroller gesteuert wird. Ein weiteres Praxisprojekt erläutert Schritt für Schritt, wie beispielsweise eine ständige Temperaturmessung mit 1-Wire-Bausteinen möglich ist.
€ 32,80
Mitglieder € 26,24
-

Elektor Publishing Das Buch der 555-Timer-Projekte
Über 45 Projekte für den legendären 555-Chip (und den 556, 568) Der 555-Timer-IC, ursprünglich um 1971 von Signetics eingeführt, gehört zweifellos zu den beliebtesten analogen integrierten Schaltkreisen, die je produziert wurden. Ursprünglich als „IC-Zeitmaschine“ bezeichnet, wurde dieser Chip über Jahrzehnte hinweg in zahlreichen zeitgesteuerten Projekten verwendet. Dieses Buch befasst sich mit der Entwicklung von Projekten, die auf dem 555-Timer-IC basieren. Es werden über 45 vollständig getestete und dokumentierte Projekte vorgestellt. Alle Projekte wurden vom Autor selbst getestet, indem sie einzeln auf einem Breadboard aufgebaut wurden. Es sind keine Programmierkenntnisse erforderlich, um die im Buch vorgestellten Projekte nachzubauen oder zu verwenden. Allerdings ist es definitiv hilfreich, über grundlegende Elektronikkenntnisse und den Umgang mit einem Breadboard zum Aufbau und Testen elektronischer Schaltungen zu verfügen. Einige der Projekte im Buch sind: Abwechselnd blinkende LEDs Veränderung der Blinkrate von LEDs Touchsensor-Ein/Aus-Schalter Ein-/Ausschaltverzögerung Lichtabhängiger Ton Dunkel-Hell-Lichtschalter Tonburst-Generator Langzeit-Timer Lauflichter LED-Roulette-Spiel Ampelsteuerung Durchgangsprüfer Elektronisches Schloss Kontaktentprellung für Schalter Spielzeug-Elektronikorgel Mehrfachsensor-Alarmsystem Metronom Spannungsmultiplizierer Elektronischer Würfel 7-Segment-Display-Zähler Motorsteuerung 7-Segment-Display-Würfel Elektronische Sirene Verschiedene andere Projekte Die im Buch vorgestellten Projekte können von den Lesern für ihre eigenen Anwendungen modifiziert oder erweitert werden. Elektronikingenieur-Studenten, Leute, die gerne kleine elektronische Schaltungen entwerfen, sowie Elektronik-Hobbyisten werden die Projekte im Buch sicher lehrreich, unterhaltsam, interessant und nützlich finden.
€ 34,80
Mitglieder identisch
-

Elektor Digital Das Buch der 555-Timer-Projekte (PDF)
Über 45 Projekte für den legendären 555-Chip (und den 556, 568) Der 555-Timer-IC, ursprünglich um 1971 von Signetics eingeführt, gehört zweifellos zu den beliebtesten analogen integrierten Schaltkreisen, die je produziert wurden. Ursprünglich als „IC-Zeitmaschine“ bezeichnet, wurde dieser Chip über Jahrzehnte hinweg in zahlreichen zeitgesteuerten Projekten verwendet. Dieses Buch befasst sich mit der Entwicklung von Projekten, die auf dem 555-Timer-IC basieren. Es werden über 45 vollständig getestete und dokumentierte Projekte vorgestellt. Alle Projekte wurden vom Autor selbst getestet, indem sie einzeln auf einem Breadboard aufgebaut wurden. Es sind keine Programmierkenntnisse erforderlich, um die im Buch vorgestellten Projekte nachzubauen oder zu verwenden. Allerdings ist es definitiv hilfreich, über grundlegende Elektronikkenntnisse und den Umgang mit einem Breadboard zum Aufbau und Testen elektronischer Schaltungen zu verfügen. Einige der Projekte im Buch sind: Abwechselnd blinkende LEDs Veränderung der Blinkrate von LEDs Touchsensor-Ein/Aus-Schalter Ein-/Ausschaltverzögerung Lichtabhängiger Ton Dunkel-Hell-Lichtschalter Tonburst-Generator Langzeit-Timer Lauflichter LED-Roulette-Spiel Ampelsteuerung Durchgangsprüfer Elektronisches Schloss Kontaktentprellung für Schalter Spielzeug-Elektronikorgel Mehrfachsensor-Alarmsystem Metronom Spannungsmultiplizierer Elektronischer Würfel 7-Segment-Display-Zähler Motorsteuerung 7-Segment-Display-Würfel Elektronische Sirene Verschiedene andere Projekte Die im Buch vorgestellten Projekte können von den Lesern für ihre eigenen Anwendungen modifiziert oder erweitert werden. Elektronikingenieur-Studenten, Leute, die gerne kleine elektronische Schaltungen entwerfen, sowie Elektronik-Hobbyisten werden die Projekte im Buch sicher lehrreich, unterhaltsam, interessant und nützlich finden.
€ 29,80
Mitglieder € 23,84
-

Elektor Publishing Das CAN-Bus Praxisbuch
Projekte mit Arduino Uno und Raspberry Pi In diesem Buch werden Anwendungen von Arduino Uno und Raspberry Pi 4 in praxisnahen Projekten auf Basis von CAN-Bus detailliert beschrieben. Durch den Einsatz von entweder Arduino Uno oder Raspberry Pi in Verbindung mit handelsüblichen CAN-Bus-Schnittstellenmodulen werden die Entwicklung, Fehlersuche und Fehlerbeseitigung sowie die Überprüfung von Projekten auf CAN-Bus-Basis erheblich erleichtert. Dieses Buch richtet sich an jeden, der mehr über den CAN-Bus lernen möchte und mit den Grundlagen der Elektronik vertraut ist. Hilfreich ist auch Erfahrung mit den Programmiersprachen C und Python sowie mit der Programmierung von Arduino Uno unter Verwendung seiner IDE und von Raspberry Pi zu haben. Das Buch ist eine nützliche Informationsquelle und ein Nachschlagewerk für jeden, der Antworten auf eine oder mehrere der folgenden Fragen sucht: Welche Bussysteme stehen für die Automobilindustrie zur Verfügung? Was sind die Grundprinzipien des CAN-Bus? Welche Arten von Frames (oder Datenpaketen) stehen in einem CAN-Bussystem zur Verfügung? Wie können Fehler in einem CAN-Bussystem erkannt werden, und wie zuverlässig ist ein CAN-Bussystem? Welche Arten von CAN-Bus-Controllern gibt es? Welches sind die Funktionsprinzipien des MCP2515 CAN-Bus-Controllers? Wie kann ich ein CAN-Bus-Projekt mit Arduino Uno realisieren? Wie kann ich Arduino oder Raspberry Pi CAN-Bus-Projekte mit 2 und 3 Knoten erstellen? Wie kann ich die Daten auf dem CAN-Bus analysieren? Wie kann ich ein CAN-Bus-Projekt mit Raspberry Pi ausführen?
€ 34,80
Mitglieder identisch
-

Elektor Digital Das CAN-Bus Praxisbuch (PDF)
Projekte mit Arduino Uno und Raspberry Pi In diesem Buch werden Anwendungen von Arduino Uno und Raspberry Pi 4 in praxisnahen Projekten auf Basis von CAN-Bus detailliert beschrieben. Durch den Einsatz von entweder Arduino Uno oder Raspberry Pi in Verbindung mit handelsüblichen CAN-Bus-Schnittstellenmodulen werden die Entwicklung, Fehlersuche und Fehlerbeseitigung sowie die Überprüfung von Projekten auf CAN-Bus-Basis erheblich erleichtert. Dieses Buch richtet sich an jeden, der mehr über den CAN-Bus lernen möchte und mit den Grundlagen der Elektronik vertraut ist. Hilfreich ist auch, Erfahrungen mit den Programmiersprachen C und Python sowie mit der Programmierung von Arduino Uno unter Verwendung seiner IDE und von Raspberry Pi zu haben. Das Buch ist eine nützliche Informationsquelle und ein Nachschlagewerk für jeden, der Antworten auf eine oder mehrere der folgenden Fragen sucht: Welche Bussysteme stehen für die Automobilindustrie zur Verfügung? Was sind die Grundprinzipien des CAN-Bus? Welche Arten von Frames (oder Datenpaketen) stehen in einem CAN-Bussystem zur Verfügung? Wie können Fehler in einem CAN-Bussystem erkannt werden, und wie zuverlässig ist ein CAN-Bussystem? Welche Arten von CAN-Bus-Controllern gibt es? Was sind die Funktionsprinzipien des MCP2515 CAN-Bus-Controllers? Wie kann ich ein CAN-Bus-Projekt mit Arduino Uno realisieren? Wie kann ich Arduino- oder Raspberry Pi-CAN-Bus-Projekte mit 2 und 3 Knoten erstellen? Wie kann ich die Daten auf dem CAN-Bus analysieren? Wie kann ich ein CAN-Bus-Projekt mit Raspberry Pi ausführen?
€ 29,80
Mitglieder € 23,84
-

Elektor Digital Das ESP32-Praxisbuch (PDF)
Die WiFi-Module der chinesischen Firma Espressif haben schon längst die Maker-Community erobert, bieten sie doch zu einem konkurrenzlosen Preis MCU- und WiFi-Funktionalität. Mit einfachen Mitteln lässt sich ein Arduino mit einem ESP-Modul um WiFi erweitern. Die globale Bastler-Gemeinde ersetzte schon bald die integrierte Firmware mit eigener Firmware, sodass Entwickler ESP-Boards wie Arduino-Boards programmieren können. Der neue ESP32 geht einen Schritt weiter und ist in jeder Beziehung leistungsfähiger als der ESP8266. Zudem besitzt er nun Bluetooth-Funktionalität. Der ESP32 verfügt über einen 240-MHz-Zweikern-Mikroprozessor mit einer Performanz von 600 DMIPS. Neben 520 KByte SRAM befinden sich 16 MByte Flashspeicher an Board. Zur Kommunikation mit der Außenwelt enthält das System-on-a-Chip die 802.11-b/g/n-WiFi-Komponente HT40 und Bluetooth-Funktionalität. Als Sensoren bietet der ESP32 einen Hall-Sensor, eine zehnfache, kapazitive Touch-Schnittstelle, einen analogen Verstärker für niedrige Signale und einen 32-kHz-Kristallquartz. Der Bestseller-Autor Erik Bartmann hat sich ausführlich mit dem ESP32 beschäftigt. Heraus gekommen ist dabei Das ESP32-Praxisbuch, in dem er die Leser Schritt für Schritt in die Arbeit mit diesem preiswerten WiFi-Mikrocontroller einführt.
€ 34,80
Mitglieder € 27,84
-

Elektor Digital Das ESP8266-Praxisbuch (E-book)
Der ESP8266 ist ein programmierbares WLAN-Funkmodul mit zahlreichen Schnittstellen wie UART, I²C und SPI. Das Board ist sehr preiswert und bereits für unter 3 Euro verfügbar. Die UART-Schnittstelle sorgt dabei für eine einfache Integration in Mikrocontrollerprojekte. Das ESP8266-Modul kann hervorragend mit dem Arduino zusammenarbeiten und ermöglicht ihm über die serielle Schnittstelle den Zugang zum Netzwerk und Internet. Es existiert eine Implementierung des ESP8266-Moduls in die Arduino-Entwicklungsumgebung. Aber auch als Standalone-Modul kann das ESP8266 eigenständig Programme abarbeiten und mit dem Internet kommunizieren, da es über einen eigenen Mikroprozessor und Speicher auf dem Board verfügt.Mittlerweile existiert auch das Entwickler-Board NodeMCU, auf dem der ESP8266-Chip mit einem USB/Seriell-Adapter versehen wurde. Mit den integrierten Sockelleisten ist ein direkter Einsatz auf üblichen Breadboards möglich. Über den USB-Anschluss wird das Board mit Strom versorgt und kann über eine Software direkt angesprochen werden. Auch das NodeMCU-Board ist sehr preiswert und bereits für unter 5 Euro zu haben.Der Bestseller-Autor Erik Bartmann hat sich ausführlich mit dem ESP8266 und dem NodeMCU beschäftigt. Heraus gekommen ist dabei Das ESP8266-Praxisbuch, in dem er die Leser Schritt für Schritt in die Arbeit mit diesen neuen, preiswerten Bauteilen einführt, mögliche technische Stolpersteine ausführlich behandelt und in zahlreichen Projekten die Praxistauglichkeit – angefangen bei einem selbst gebauten Webserver bis hin zu klugen Relay-Ansteuerung – belegt.
€ 34,80
Mitglieder € 27,84
-

Elektor Bundles Das MakePython ESP32 Development Kit
Lernen Sie, wie Sie den ESP32-Mikrocontroller und die MicroPython-Programmierung in Ihren zukünftigen Projekten einsetzen können! Das Projektbuch – geschrieben von Dogan Ibrahim – enthält viele Software- und Hardware-basierte Projekte, die speziell für das MakePython ESP32 Development Kit entwickelt wurden. Das Kit wird mit verschiedenen LEDs, Sensoren und Aktoren geliefert. Ziel des Kits ist es, grundlegende Kenntnisse für die Erstellung von IoT-Projekten zu erwerben. Die in diesem Buch vorgestellten Projekte sind umfassend getestet und funktionsfähig und verwenden alle mitgelieferten Komponenten. Für jedes Projekt gibt es im Buch ein Blockdiagramm, einen Schaltplan, ein vollständiges Programmlisting und eine komplette Programmbeschreibung. Lieferumfang des Kits 1x MakePython ESP32-Entwicklungsboard mit LCD 1x Ultraschall-Entfernungsmodul 1x Temperatur- und Feuchtigkeitssensor 1x Buzzer-Modul 1x DS18B20-Modul 1x Infrarotmodul 1x Potentiometer 1x WS2812-Modul 1x Schallsensor 1x Vibrationssensor 1x Lichtempfindliches Widerstandsmodul 1x Pulssensor 1x Servomotor 1x USB-Kabel 2x Taste 2x Steckplatine 45x Schaltdraht 10x Widerstand 330R 10x LED (Rot) 10x LED (Grün) 1x Projektbuch (Deutsch, 213 Seiten) 46 Projekte im Buch LED-Projekte Blinkende LED Blinkendes SOS Blinkende LED – mit einem Timer Abwechselnd blinkende LEDs Tastersteuerung Ändern der LED-Blinkrate durch Taster-Interrupts Laufschrift-LEDs Binär zählende LEDs Weihnachtsbeleuchtung (zufällig blinkende 8 LEDs) Elektronischer Würfel Glücklicher Tag der Woche Pulsweitenmodulation (PWM) Projekte Erzeugt eine 1000-Hz-PWM-Wellenform mit 50% Tastverhältnis Steuerung der LED-Helligkeit Messung der Frequenz und des Tastverhältnisses einer PWM-Wellenform Melodie-Macher Einfache elektronische Orgel Steuerung eines Servomotors Servomotor DS18B20 Thermometer Analog-Digital-Wandler (ADC) Projekte Spannungsmesser Aufzeichnung der analogen Eingangsspannung ESP32 interner Temperatursensor Ohmmeter Lichtempfindliches Widerstandsmodul Digital-Analog-Wandler (DAC) Projekte Erzeugung von Festspannungen Erzeugen eines Sägezahnsignals Erzeugen eines Dreieckssignals Arbiträre periodische Wellenform Generierung eines Sinussignals Erzeugung eines genauen Sinussignals mit Hilfe von Timer-Interrupts Verwendung des OLED-Displays Sekundenzähler Ereigniszähler DS18B20 OLED-basiertes Digitalthermometer ON-OFF Temperaturregler Messung der Temperatur und Luftfeuchtigkeit Ultraschall-Entfernungsmessung Höhe einer Person (Stadiometer) Messung der Herzfrequenz (Puls) Andere mit dem Kit gelieferte Sensoren Alarm bei Diebstahl Tonaktiviertes Licht Infrarot-Hindernisvermeidung mit Summton WS2812 RGB-LED-Ring Zeitstempel für Temperatur- und Luftfeuchtigkeitswerte Netzwerk-Programmierung WLAN-Scanner Fernsteuerung über den Internetbrowser (mit einem Smartphone oder PC) – Webserver Speichern von Temperatur- und Luftfeuchtigkeitsdaten in der Cloud Low-Power-Betrieb Aufwecken des Prozessors mit einem Timer
-
Elektor Digital Das MQTT-Praxisbuch (PDF)
MQTT ist ein leichtgewichtiges, ereignis- und nachrichtenorientiertes Protokoll zur effizienten und asynchronen Kommunikation zwischen Geräten auch über limitierte Netzwerke. Das bereits 1999 von IBM entwickelte Protokoll eignet sich heute in besonderer Weise für Internet-of-Things-Anwendungen. Im Gegensatz zu HTTP mit Request/Response-Verfahren ist bei MQTT eine Publish/Subscribe-Architektur umgesetzt. Es stehen mittlerweile zahlreiche MQTT-Broker und -Clients zur Verfügung. Aufgrund der Unterstützung durch die Eclipse Foundation, IBM und vieler anderer stehen zahlreiche Komponenten kostenlos im Internet zur Verfügung. Client-Bibliotheken gibt es für die unterschiedlichsten Plattformen und Programmiersprachen. Unterstützt werden u. a. die PC-Plattform mit Java und .Net sowie Arduino und Raspberry Pi. Das MQTT-Praxisbuch führt Schritt für Schritt in die praktische Arbeit mit diesem ressourcensparenden Protokoll ein. Dabei widmet der Autor Walter Trojan dem Thema IoT-Sicherheit ein ausführliches Kapitel. Anhand von abgeschlossenen Projekten zum Nachbauen stellt der Autor in beeindruckender Weise die praktische Bedeutung des MQTT-Protokolls in modernen IoT-Anwendungen dar: MQTT auf ESP8266 MQTT mit Arduino-IDE MQTT-Benchmarks MQTT auf dem Raspberry Pi Flow-Programmierung mit Node-RED Boss aller Automaten: openHAB Projekt Gewächshaus mit automatisierter Beleuchtung, Bewässerung, Temperaturregelung sowie Luft- und Erdfeuchtigkeitsmessung
€ 32,80
Mitglieder € 26,24
-

Elektor Digital Das MSP430 Mikrocontroller Buch (E-book)
Moderne Mikrocontroller werden immer leistungsfähiger und können vielfältige Aufgaben übernehmen, für die vor wenigen Jahren noch ein kompletter Computer nötig gewesen wäre. Gerade für die Entwicklung tragbarer Geräte bringt die Prozessorfamilie der MSP430-Mikrocontroller von Texas Instruments alle nötigen Peripheriekomponenten integriert mit, um ohne aufwendige externe Beschaltung komplexe Funktionen einfach zu realisieren. Die RISC-Architektur des Prozessors ist dabei ganz auf Rechengeschwindigkeit, aber gleichzeitig auch auf Energie-Effizienz getrimmt.Dieses Buch eröffnet einen schrittweisen Einstieg in die Welt der Mikrocontrollerprogrammierung und führt mit ausführlichen Anwendungsbeispielen in die Fähigkeiten dieser außergewöhnlichen Prozessorfamilie ein. Jede Komponente des Prozessors wird ausführlich erklärt und deren Funktion in kleinen Beispielprogrammen gleich umgesetzt. Abgerundet wird jedes Kapitel mit einigen Übungsaufgaben. So entsteht neben dem eigentlichen Lerneffekt gleichzeitig eine Referenzbibliothek von Funktionsmodulen, die später in eigenen Anwendungen leicht weiter verwendet werden können.DownloadsDie Listings der im Buch beschriebenen Programmbeispiele (ausschließlich in 'C') und weitere Infos finden Sie hier.
€ 39,80
Mitglieder € 31,84























